Financial statements based on a reporting system other than GAAP are said to be prepared using other comprehensive basis of accounting (OCBOA)
Other comprehensive basis of accounting other than GAAP may be:
- The cash basis and modifications of the cash basis having substantial support
- A basis used for tax purposes
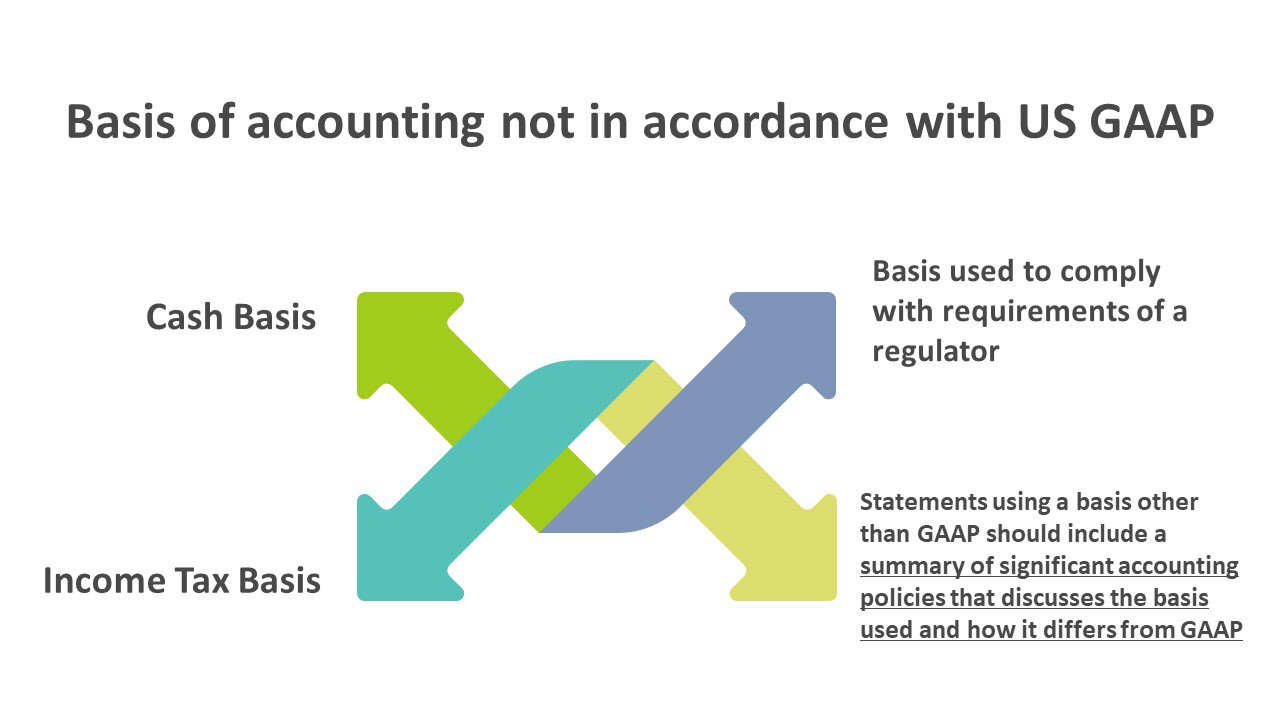
- A basis used to comply with the requirements of a regulator
Statements prepared using an OCBOA should include a summary of significant accounting policies, including discussion of the basis used and how it differs from GAAP
Cash Basis
Under cash basis of accounting, revenues and expenses are recognized when cash is received or paid, respectively, regardless of when goods are received or services are rendered
- Cash basis of accounting ignores the revenue recognition and matching principles that are fundamental to the accrual basis
- Cash basis financial statements do not conform to GAAP
Modified Cash Basis
The modified cash basis uses the cash basis for typical operating activities with modifications having substantial support, for eg., reporting inventory, accruing income taxes, and capitalizing and depreciating fixed assets
- Professional services firms such as physicians, realtors, and architects generally follow modified cash basis
- Modified cash basis financial statements do not conform to GAAP
Income Tax Basis
This basis must be applied to calculate income tax liability
Certain principles underlying the tax code differ in significant ways from those in the conceptual framework for financial accounting
Hence, financial statements prepared under GAAP are not usable for calculating income tax liability
If you have found this blog to be useful, you may share with your friends. Thanks!