Value Creation Through Connection!
Offering value through connection is a critical aspect of managing a team successfully. Through understanding how to connect with your team, motivate them, and engaging with them in an authentic manner, you can create a high top-notch environment that encourages high performance. People Business To engage with team members in an authentic manner, you must […]
Continue reading→Derivatives and Hedge Accounting
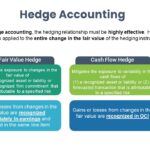
Derivatives A call (put) option is the right to purchase (sell) an asset at a fixed price (i.e., the exercise price or the strike price) on or before a future date (i.e., expiration date). A forward contract is an agreement for the purchase and sale of a stated amount of a commodity, foreign currency, or […]
Continue reading→Governmental Accounting – Reporting
1. Governmental Funds Reporting Governmental funds emphasize sources, uses, and balances of current financial resources. Major vs. nonmajor fund reporting. The focus of governmental and enterprise fund financial statements is on major funds. Each major fund is presented in a separate column. The main operating fund (i.e., the general fund) is always reported as a […]
Continue reading→Comprehensive Annual Financial Report
The comprehensive annual financial report covers all funds and activities of the primary government and provides an overview of the discretely presented component units of the reporting entity. The comprehensive annual financial report includes introductory, financial, and statistical sections. The financial section includes management’s discussion and analysis (MD&A). MD&A is required supplementary information. It is […]
Continue reading→Governmental Accounting – Reporting Entity, Basis of Accounting, and Funds
The reporting entity consists of the primary government and its component units, which is a legally separate organization for which the primary government is responsible. The basis of accounting is the timing of the recognition of economic events or transactions. Measurement Focus is what is measured and tracked. Governmental funds use a modified accrual basis. […]
Continue reading→Asset Retirement Obligation
An Asset Retirement Obligation (ARO) relates to a legal obligation arising from the acquisition, construction, development, or normal operation of an asset Initial Recognition and Measurement The associated Asset Retirement Cost is added to the carrying amount of the asset when an ARO is recognized The fair value of the ARO liability is recognized when […]
Continue reading→Extinguishment of Debt
Issuers sometimes retire debt before matutiry, for eg., to eliminate high-interest debt when rates are declining or to improve debt ratios All extinguishment of debt before scheduled maturities are fundamentally alike and should be accounted for similarly The net carrying amount is the amount due at maturity, adjusted for Unamortized premium (discount), and Cost of […]
Continue reading→Warrant Bonds
Securities with characteristics of liabilities and equity are convertible debt that may be exchanged for common stock of the issuer When the debt and equity elements of convertible debt are treated as inseparable, the entire proceeds should be accounted for and reported as a liability until conversion Warrants allow a debtholder to obtain common shares […]
Continue reading→Income Tax Accounting
The asset and liability approach is used to account for income taxes The tax consequences of some transactions or events may be recognized in income taxes currently payable or refundable in a year different from that in which their financial statement effects are recognized (temporary differences) Also, some transactions or events may have tax consequences […]
Continue reading→Warranties
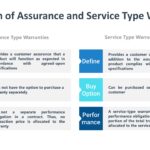
A warranty is a written agreement of the integrity of a product or service and an undertaking by the seller to: Repair or replace a product Refund all or part of the price, or Provide additional service A warranty is customarily offered for a limited time, such as 2 years. It may or may not […]
Continue reading→