Estate Planning Roadmap: Wills, Trusts & Executor Duties Secure Your Legacy. Simplify the Process. Why Estate Planning Is A Must Estate planning isn’t just for the wealthy. It’s for anyone who wants to protect their loved ones, minimize confusion, and leave behind a meaningful legacy. 🧠 “Estate planning is about more than money. It’s about […]
Continue readingCategory Archives: Us Income Tax
FICA and FUTA
FICA taxes are imposed on both employers and employees. FUTA taxes are imposed on employers only. FICA Employers and employees are each liable for FICA taxes. Under Sec. 3102(a), an employer is liable for collecting (withholding) the employees’ tax from wages. Employers who fail to collect these taxes are responsible for the employees’ tax, in […]
Continue readingCredits
Nonrefundable Tax Credits (1) Foreign Tax Credit (2) Child and Dependent Care Credit (3) Lifetime Learning Credit (4) Retirement Savings Contribution Credit (5) Child and Other Dependents Tax Credit (6) Credit for the Elderly or the Disabled (7) General Business Credit (8) Adoption Credit Refundable Tax Credits (1) Credit for Taxes Withheld (2) Earned Income […]
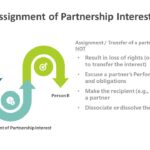
Continue readingAssignment of Partnership Interest
Transfer of a partner’s interest does not Result in loss of rights (other than the right to transfer the interest) Excuse a partner’s performance of duties and obligations Make the recipient (e.g., a person or estate) a partner Dissociate or dissolve the partnership Partnership rights may be assigned without the dissolution of the partnership. The […]
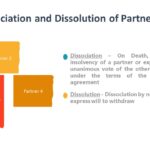
Continue readingDissociation and Dissolution of Partnership
Dissolution Dissolution can occur by an agreement of the partners to end the partnership. Although the actual authority to act on behalf of the partnership ceases at dissolution, apparent authority to conduct business in the usual way continues until notice is given to third parties or the partnership business winds up. A partner’s liability for […]
Continue readingGeneration Skipping Transfer Tax
The Generation-Skipping Transfer Tax is imposed separately and in addition to gift and estate taxes on transfers directly or in trust for the sole benefit of a person at least two generations younger than the transferor. A generation-skipping transfer is defined as a taxable termination, a taxable distribution, or a direct skip [Sec. 2611(a)]. A […]
Continue readingEstate Income Tax vs Estate Tax
Estate Income Tax Estate Income Tax – Imposed on the income of estates. Imposed on the estate level or beneficiary level An estate (or trust) with a gross income of at least $600 is required to file Form 1041, Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts, no later than the 15th day of the 4th month […]
Continue readingGift Tax
The gift tax is a tax of the transfer of a gift imposed on the donor. A gift is complete when the donor has so parted with dominion and control as to leave him or her no power to change its disposition. The amount of a gift made in property is the fair market value […]
Continue readingSimple and Complex Trusts
Simple Trust – A simple trust is formed under an instrument that (1) requires current distribution of all its income, (2) requires no distribution of the res (i.e., principal, corpus), and (3) provides for no charitable contributions by the trust. Complex Trust – A Complex Trust is a Trust that permits accumulation of current income, […]
Continue readingInvoluntary Conversions
A taxpayer may elect to defer recognition of gain if property is involuntary converted into money or property that is similar or related in service or use. An involuntary conversion of property results from destruction, theft, seizure, requisition, condemnation, or threat of imminent requisition or condemnation. When a property is converted involuntarily into nonqualified proceeds […]
Continue reading