The COSO Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework provides a basis for coordinating and integrating all of an organization’s risk management activities. Effective integration (1) improves decision making and (2) enhances performance
ERM is based on the premise that every organization exists to provide value to its stakeholders. ERM is defined as “the culture, capabilities, and practices, integrated with strategy-setting and performance, that organizations rely on to manage risk in creating, preserving, and realizing value”
Effective ERM can
1) Increase the range of opportunities
2) Identify and manage risk entity-wide
3) Increase positive outcome
4) Reduce performance variability
5) Improve resource deployment
6) Enhance enterprise resilience
Does your organization have an effective risk management strategy? Do you need our help?
Risk must be considered in setting strategy, business objectives, performance, targets, and tolerance.
a) Strategy communicates how the organization will (a) achieve its mission and vision (b) apply its core values
b) Business objectives are the measurable steps taken to achieve the strategy
c) Tolerance is the range of acceptable variation in performance results
The organization considers the effect of strategy on its risk profile
The risk profile is a composite view of the types, severity, and interdependencies of risks related to a specific strategy or business objective and their effect on performance. A risk profile may be created at any level (eg entity, division, operating unit, or function) or aspect (eg product, service, or geography) of the organization
Have you mapped the risk profile for your organization? Do you need our help?
ERM Roles and Responsibilities
a) The board provides risk oversight of ERM culture, capabilities, and practices
Certain board committees may be formed for this purpose. Eg are 1) An audit committee 2) A risk committee 3) An executive compensation committee, and 4) A nomination or governance committee
b) Management has overall responsibility for ERM and is generally responsible for the day-to-day managing of risk, including the implementation and development of the COSO ERM framework
Three lines of management accountability
1) Principal owners of risk. They manage performance and risks taken to achieve strategy and objectives
2) Supporting (business-enabling) functions that (a) provide guidance on performance and ERM requirements (b) evaluate adherence to standards (c) challenge the first line to take prudent risks
3) Assurance functions that (a) perform audits (reviews) of ERM (b) Identify issues and improvements (c) make recommendations, and (d) inform the board and executives of matters needing resolution
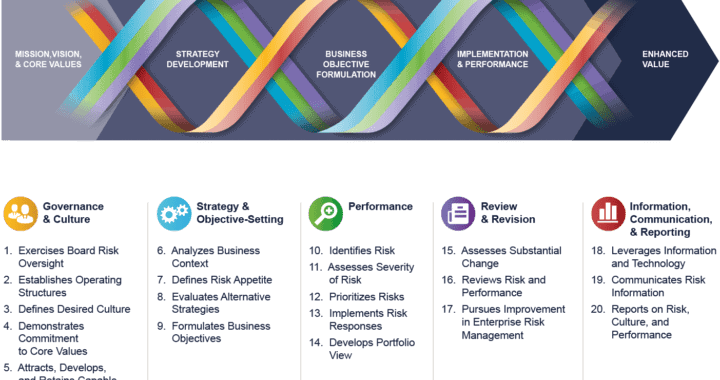
ERM Components
The COSO ERM framework consists of 5 interrelated components
1. GOVERNANCE AND CULTURE
a) Exercises board risk oversight
b) Establishes operating structures
c) Defines desired culture
d) Demonstrates commitment to core values
e) Attracts, retains, and develops capable individuals
2. STRATEGY AND OBJECTIVE SETTING
a) Analyzes business context
b) Defines risk appetite
c) Evaluate alternative strategies
d) Formulates business objectives
3. PERFORMANCE
a) Identifies risk
b) Assesses severity of risk
c) Prioritizes risk
d) Implements risk responses
e) Develops portfolio view
4. REVIEW AND REVISION
a) Assess substantial change
b) Review risk and performance
c) Pursue improvement in enterprise risk management
5. INFORMATION, COMMUNICATION, AND REPORTING
a) Leverages information and technology
b) Communicates Risk Information
c) Reports on risk culture and performance
Does your organization have the ERM components implemented? Do you need our help?
ERM limitations result from the possibility of human error, cost-benefit considerations, simple errors, and mistakes, collusion, and inappropriate management override.
ERM may be applied to manage and adapt to environmental, social, and governance risks.
COSO outlines below mentioned eight-step approach for the implementation of an effective ERM program.
1) Seek board and senior management involvement and oversight
2) Identify and position a leader to drive ERM initiative
3) Establish a management working group
4) Inventory the existing risk management practices
5) Conduct an initial assessment of key strategies and related strategic risks
6) Develop a consolidated action plan and communicate to board and management
7) Develop and/or enhance risk reporting
8) Develop the next phase of action plans and ongoing communications
If you have found this blog to be useful, you may share with your friends. Thanks!