The COSO framework consists primarily of:
- A definition of internal control
- Categories of objectives
- Components and related principles, and
- Requirements of an effective system of internal control
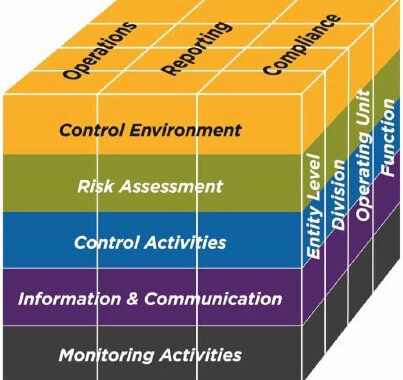
Internal Control
Categories of Objectives
- Operations objectives relate to achieving the entity’s mission and safeguarding assets
- Reporting objectives relate to the entity’s preparation of financial and nonfinancial reports for the organization and stakeholders
- Compliance objectives relate to the entity’s adherence to applicable laws, rules, and regulations
Components of Internal Control
- Control Environment – (Standards, Processes, and Structure)
5 principles related to control environment are:
-
- Commitment to integrity and ethical values
- Board independence and oversight
- Management establishment of structures and responsibilities
- Commitment to attract, develop, and retain competent individuals
- Accountability
- Risk Assessment – (Risks to achieving organizational objectives)
4 principles related to risk assessment are:
-
- Specification of objectives
- Identification and analysis of risks
- Consideration of potential for fraud
- Identification and assessment of changes
- Control Activities – (Policies and procedures to help mitigate risks)
3 principles related to control activities are:
-
- Selection and development of control activities
- Selection and development of control activities over technology
- Deployment of control activities through policies and procedures
- Information and communication – (Information system to obtain, generate, use, and communicate information)
3 principles related to information and communication are:
-
- Obtainment, generation, and use of relevant quality information
- Internal communication of information
- Communication with external parties
- Monitoring – (Assessment of the quality of interna control performance over time)
2 principles related to monitoring are:
-
- Ongoing or separate evaluations
- Evaluation and communication of control deficiencies in a timely manne
Have you set up a framework of internal control? We can help
Internal Control and Fraud
There are 3 areas of fraud:
- Fraudulent external financial reporting
- Misappropriation of assets
- Illegal acts
Fraud Management Program
The components of effective fraud management program includes the following:
- Company ethics policy
- Fraud awareness
- Fraud risk assessment
- Ongoing reviews
- Prevention and detection
- Investigation
Control Environment includes elements as a code of conduct, ethics policy, or fraud policy to set the appropriate tone at the top; hiring and promotion guidelines and practices; and board oversight.
Fraud awareness is understanding the nature, causes, and characteristics of fraud. It is developed through periodic fraud risk assessments, training of employees, and communications between management and employees.
Do you have an effective fraud management program in place? We can help
If you have found this blog to be useful, you may share with your friends. Thanks!