Depreciation systematically and rationally allocates the historical cost of the productive capacity of a tangible capital asset to the periods benefited. It is a process of allocation not of valuation
Depreciation does not set aside funds, and hence, an accumulated depreciation account is not a reserve (It is a contra-asset account)
Depreciation is not always expensed.
Depreciable Base - Historical cost minus the salvage value
Estimated Useful Life - Depends on the causes of depreciation and the entity's intended use. It may be expressed in units of time, machine hours, or units of output
Salvage Value - An estimate of the amount that will be realized at the end of the useful life of a depreciable asset
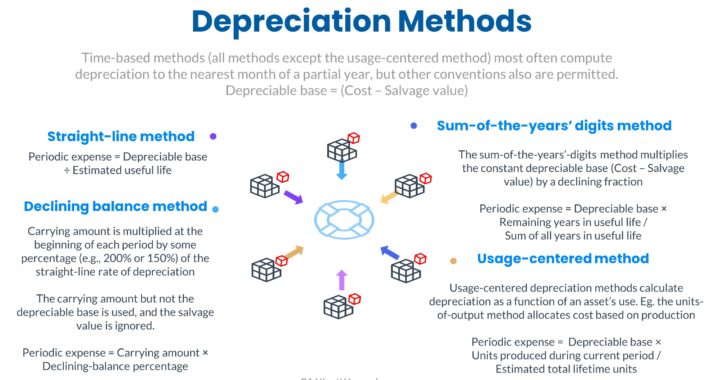
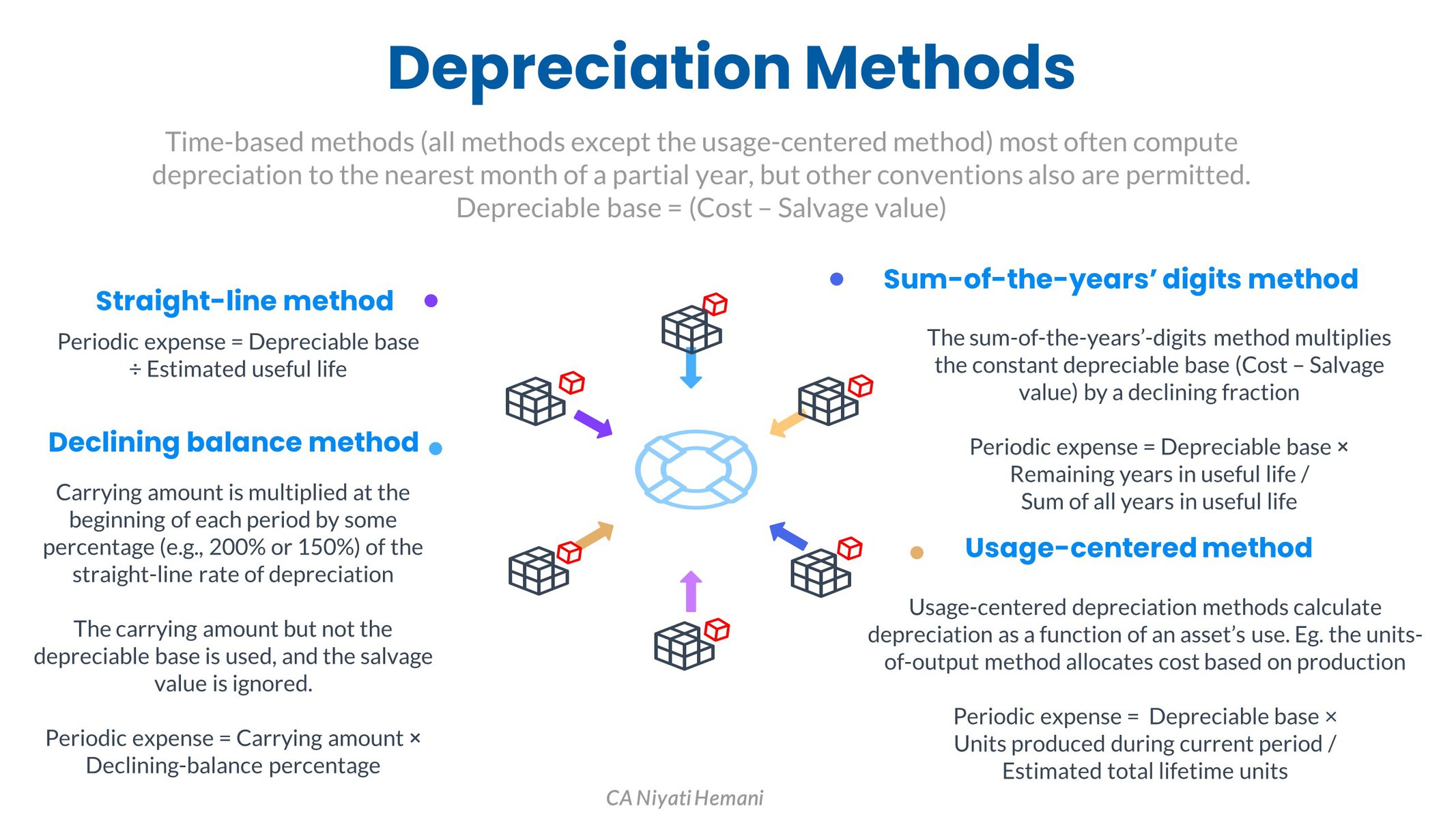
- Straight-line Method - Depreciation expense is recognized evenly over the estimated useful life of the asset [ (Cost - Salvage Value) / Estimated Useful Life ]
- Accelerated Methods - Depreciation expense is higher in the early years of the asset's useful life and lower in the later years. Annual depreciation is computed by multiplying the book value at the beginning of the fiscal year by a multiple of the straight-line rate of depreciation. In this method, book value is not reduced by the salvage value
- Sum of Years Digits - The depreciation expense fraction is based on the estimated life, the sum of years digits in reverse order
- Usage Centered Depreciation - Based on Units of output or service used - [ Depreciation Base * number of units produced / total estimated units to be produced ]
- Group or Composite Depreciation - This method uses straight-line techniques for an aggregate of assets - a) The composite method relates to groups of dissimilar assets with varying useful lives, and b) The group method deals with similar assets
Disclosure
Full disclosure should be made of depreciation methods and practices, including;
- Depreciation expense for the period
- Balances of major classes of depreciable assets by nature or function
- Accumulated depreciation either by major class or in total
- Description of depreciation methods for each major class of assets
If you have found this blog to be useful, you may share with your friends. Thanks!