GAAP gave the option to entities to:
- Measure most financial assets and liabilities at fair value, and
- Report unrealized gains and losses in earnings
The decision of whether to elect the fair value option is made irrevocably at an election date. The decision is made instrument by instrument
The fair value option need not be applied to all instruments in a single transaction. For eg. it may be applied to some select shares or bonds acquired in a transaction
Fair value option cannot be elected to the following items:
- An investment that requires to issue consolidated financial statements
- Obligations for post-retirement employee benefits
- Financial assets and liabilities under leases
- Demand deposit liabilities
- Financial instruments at least partly classified in equity
An entity may choose to elect Fair Value Option for an investment in investee where it could have elected to account the investments under the equity method
Financial Statement Presentation
Balance Sheet
Assets and liabilities measured using the fair value option are reported in a way that separates their fair values from the carrying amount of similar items measured using another attribute
Income Statement
Unrealized gains and losses on items measured using the fair value option are recognized as earnings in the income statement
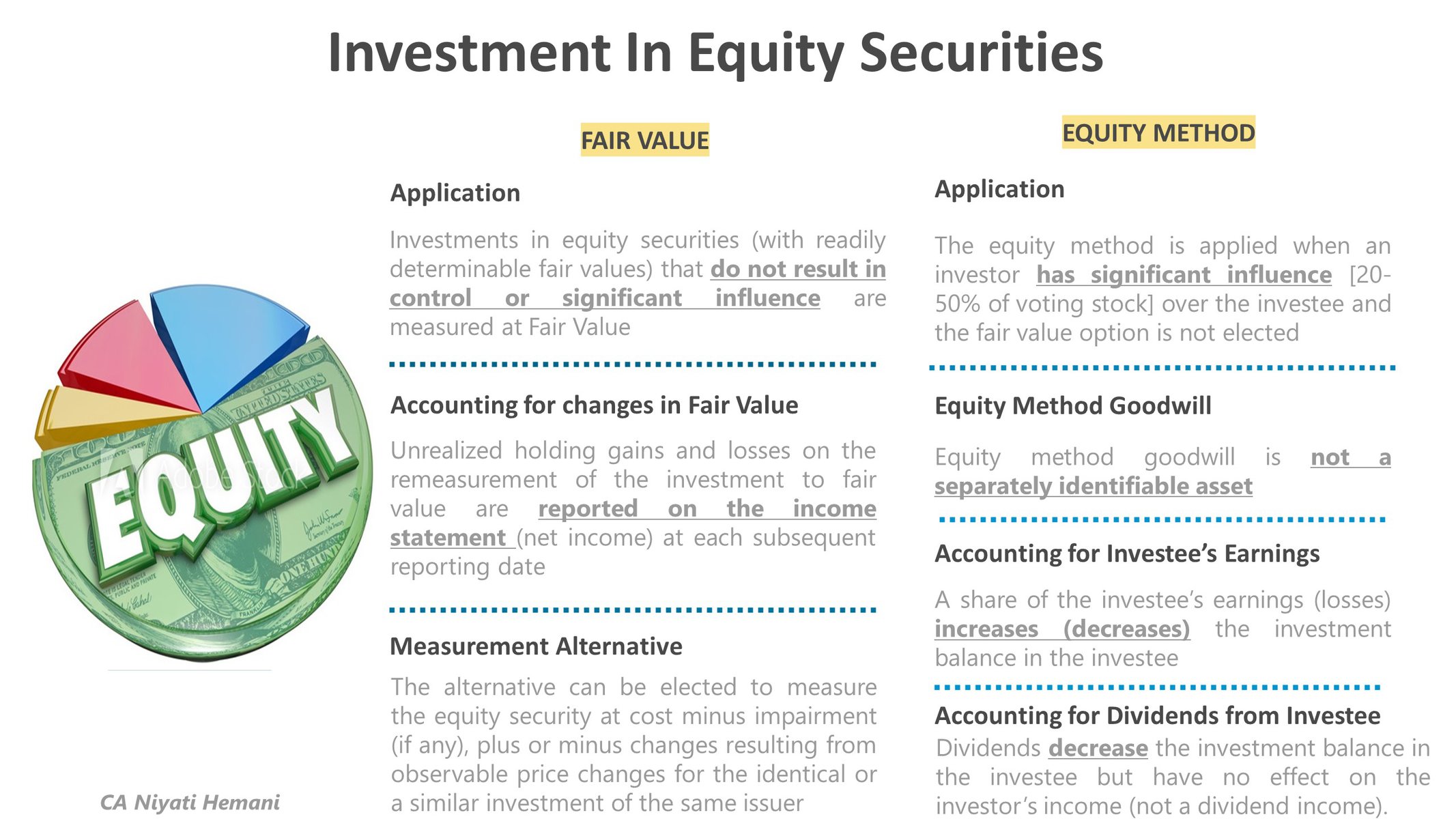
Investments in Equity Securities
The accounting method for investment in voting stock depends on the presumed influence that the investor has over the investee. The presumed influence is determined based on the ownership interest held
Percentage Ownership Presumed Influence Accounting Method
<20% Little or none Fair Value Method
= 20% <= 50% Significant Influence Equity Method or Fair Value Option
> 50% Control Consolidation
Measurement of an Investment in Equity Securities
The investment is measured at fair value at each balance sheet date
Unrealized holding gains and losses on the re-measurement of the investment to fair value are reported in the income statement at each subsequent reporting date
Dividends received from investments in equity securities are reported as dividend income in the income statement
Measurement of Investment in Equity Securities without readily determinable fair value
An entity may elect a measurement alternative for an investment in equity securities without a readily determinable fair value
This alternative is cost minus impairment (if any), plus or minus changes resulting from observable price changes for the identical or similar investment of the same issuer
The entity must reassess at each reporting period whether the fair value of an equity investment is readily determinable
Impairment Test
A qualitative assessment of whether an investment is impaired must be performed at each reporting date
An investment is impaired if the fair value of the investment is lower than its carrying amount
Equity Method
An investment in common stock enabling the investor to exercise significant influence over the investee should be accounted for by the equity method (assuming no FVO election is made)
An equity method investment is initially recognized at cost. The price paid by an investor to acquire shares in an investee may differ from the underlying book value (i.e. the investee's net assets per its financial statements) it represents
The difference may be on account of
- Premium paid (i.e. goodwill) by the investor to acquire the investment
- Discrepancies between the investee's recognized net assets at book values and at current fair values
- Unrecognized assets in the books of the investee
Equity Method Goodwill
Goodwill resulting from the acquisition is the difference between the cost of the investment and the investor's equity in the fair value of the investee's net assets
Equity Method goodwill is included in the carrying amount of the equity method investment
Equity method investment is tested for impairment
Applying the Equity Method
Under the equity method, the investor recognizes in income its share of the investee's earnings or losses in the periods for which they are reported by the investee
Thus, the equity method involves:
- Increasing the original cost of the Investment by the investor's pro-rata share of the investee's earnings
- Decreasing the original cost of the investment:
- By the investor's share of the investee's losses, and
- For dividends paid (treated as a return on investment)
Thus, under the equity method the investment account moves as below:
Carrying Value of the Investment (Opening)
+ Share of Investee's net income (loss)
- Dividends received
___________________________________
= Carrying Value of the Investment (Closing)
___________________________________
The investor share of investee losses in excess of the carrying value on investment
An equity method investment would not be permitted to have a negative balance since the investor enjoys limited liability. When the investment account reaches a zero balance, discontinue the application of the equity method and make only disclosures in the notes.
If the investor later returns to profitability, the investor should ignore its share of earnings until the previously ignored losses have been fully offset
Change to Equity Method - Increase in Level of Ownership
When significant influence is achieved in stages, the investor applies the equity method prospectively from the moment the significant influence is achieved
Change from Equity Method
If an investor can no longer be presumed to exercise significant influence, it ceases to account for the investment using the equity method
If you have found this blog to be useful, you may share with your friends. Thanks!