Software Accounting
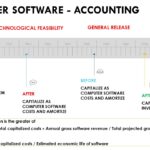
Accounting for the costs of developing or obtaining computer software depends on whether the software is (1) sold to external customers or (2) used internally Costs of software may be a) Expensed as incurred b) Capitalized as computer software costs, or c) Included in the inventory Costs of software to be used internally are either […]
Continue reading→Franchisee Accounting
A franchise is a contractual agreement by a franchisor to permit a franchisee to operate a certain business Franchisee Accounting The franchisee should capitalize the costs of acquiring the franchise such as the initial fee and other expenditures (eg. legal fees) incurred to acquire the franchise Franchise costs are amortized over their estimated useful life […]
Continue reading→Goodwill
Goodwill is recognized only in a business combination It is an asset representing the future economic benefits arising from other assets acquired in a business combination that are not individually identified and separately recognized The initially recorded amount is the difference between the cost of the enterprise acquired and the sum of the assigned costs […]
Continue reading→Intangible Assets
Intangible Assets lacks physical substance Intangible assets may convey to the holder a contractual or legal right to receive future economic benefits (eg. patents, leaseholds, or franchises) Another type of intangible asset reflects costs not assignable to specific products or services but that are expected to have future economic benefits (eg. customer lists, noncontractual customer […]
Continue reading→Impairment Of Long Lived Assets
This applies to the long-lived assets of an entity that are to be held and used or disposed of Although lower cost or market rule does not apply to Property, Plant, and Equipment, their permanent decline in value should be recognized Impairment is the condition that exists when the carrying amount of a long-lived asset […]
Continue reading→Exchange of Assets
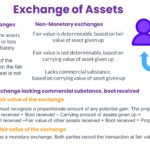
Exchanges are measured at fair value Monetary exchanges – are measured at the fair value of the assets involved, with gain or loss recognized immediately Nonmonetary exchange of assets – is treated as a monetary exchange when the fair value of both the assets is determinable The asset received is measured at the fair […]
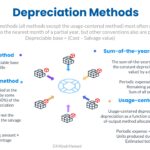
Continue reading→Depreciation Methods
Depreciation systematically and rationally allocates the historical cost of the productive capacity of a tangible capital asset to the periods benefited. It is a process of allocation not of valuation Depreciation does not set aside funds, and hence, an accumulated depreciation account is not a reserve (It is a contra-asset account) Depreciation is not always […]
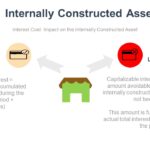
Continue reading→Internally Constructed Asset
The costs capitalized when productive assets are constructed may be direct or indirect. Internally constructed assets should be capitalized at the lower of their fair value or its cost If cost exceeds fair value, the excess is expensed immediately to avoid overstating the asset Qualifying Asset Qualifying Assets are assets for which interest must be […]
Continue reading→Bond Investments
A bond is a formal contractual agreement by an issuer to pay an amount of money (face amount) at the maturity date plus interest at the stated rate at specific intervals. All items are stated in a document called an indenture The investor in a bond may elect FVO since the bond is a financial […]
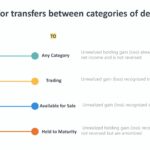
Continue reading→Transfer between categories of debt securities
Transfer between categories of debt securities is accounted for at transfer date fair value. The following describes the treatment of unrealized holding gains and losses at that date: From To […]
Continue reading→