Debt Securities
A debt security represents a creditor relationship with the issuer In addition to the common forms of debt, this category includes: Mandatorily redeemable preferred stock Preferred stock redeemable at the investor’s option Collateralized mortgage obligations Classification Debt securities are classified at acquisition into one of the three categories. The classification is reassessed at each reporting […]
Continue reading→Fair Value And Equity Method Of Valuing Equity Investments
GAAP gave the option to entities to: Measure most financial assets and liabilities at fair value, and Report unrealized gains and losses in earnings The decision of whether to elect the fair value option is made irrevocably at an election date. The decision is made instrument by instrument The fair value option need not be […]
Continue reading→Fair Value Measurements
GAAP establishes a framework for fair value measurements (FVMs) required by other pronouncements. Accordingly, they Define fair value Discuss valuation techniques Establish a fair value hierarchy of inputs to valuation techniques, and Require expanded disclosures about FVMs Fair value is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a […]
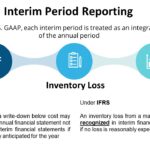
Continue reading→Interim Period Reporting
Each interim period is treated primarily as an integral part of an annual period. Ordinarily, the results for an interim period should be based on the same accounting principles the entity uses in annual statements, but certain principles may require modification at interim dates. Inventory Measurement at Interim Dates A Write down of inventory below […]
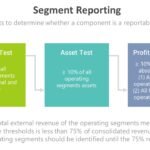
Continue reading→Segment Reporting
The objective of segment reporting is to provide information about the different business activities of the entity and the economic environments in which it operates. An operating segment has three characteristics: It is a business component of an entity that may recognize revenues and incur expenses Its operating results are regularly reviewed by the entity’s […]
Continue reading→Recognition Of Revenue Over Time
For each performance obligation satisfied over time, an entity must recognize revenue over time For this purpose, the entity measures the progress toward complete satisfaction using: Output method; or Input method To determine the appropriate method, an entity must consider the nature of the good or service that it promised to transfer to the customer […]
Continue reading→Variable Consideration
If a contract includes a variable amount, an entity must estimate the consideration to which it will be entitled in exchange for transferring the promised goods or services to a customer. The contract price may vary for the following reasons: Refunds due to a right of return provided to customers Sales Incentives Prompt payment discounts […]
Continue reading→Error Correction
An error in the prior statement results from: A mathematical mistake A mistake in the application of GAAP; or An oversight or misuse of facts existed when the statements were prepared A change to a generally accepted accounting principle from one that is not an error correction is not an accounting change An error related […]
Continue reading→Pension Plans
Pension Plans A pension plan is a separate accounting entity to which a sponsoring employer makes contributions in order to provide employees retirement benefits in exchange for current or past services Pension benefits are a form of deferred compensation and hence, they are not paid currently. They are paid to retired employees, on a periodic […]
Continue reading→Basis of Accounting
Financial statements based on a reporting system other than GAAP are said to be prepared using other comprehensive basis of accounting (OCBOA) Other comprehensive basis of accounting other than GAAP may be: The cash basis and modifications of the cash basis having substantial support A basis used for tax purposes A basis used to comply […]
Continue reading→