Business Nexus for Sales Tax
For a taxing authorities to tax sales and income-generating activities, nexus is required to be established of a physical and/or financial presence within a jurisdiction. Here are the 5 drivers in establishing the nexus … A physical location in the state Resident employees working in the state Real or intangible property (owned or rented) within […]
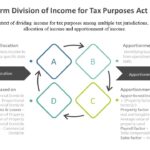
Continue reading→The Uniform Division of Income for Tax Purposes Act (UDITPA)
Before a state can tax a non resident, a minimum presence in the taxing state by the non resident must be established. In the context of Uniform Division of Income for Tax Purposes, income is distributed among multiple tax jurisdictions by allocation of income and apportionment of income. In the context of dividing income for […]
Continue reading→Exempt Organizations in US
1 EXEMPT STATUS Exempt status generally depends on the nature and purpose of an organization. An organization is tax-exempt only if it is a class specifically described by the IRC as one on which exemption is conferred. An organization operated for the primary purpose of carrying on a trade or business for profit is generally […]
Continue reading→Unrelated Business Income Tax (UBIT)
UNRELATED BUSINESS INCOME TAX Unrelated business income (UBI) is income from a trade or business, regularly carried on, that is not substantially related to the charitable, educational, or other purpose constituting the basis for an organization’s tax-exempt status. But income is not subject to tax as UBI if substantially all the work is performed […]
Continue reading→S Corporation Election and Termination
ELECTION All eligible corporation must make the election for S Corporation status by filing Form 2553 All shareholders at the time the election is made must file a consent Each person who was a shareholder at any time during the part of the tax year before the election is made must also consent. If any […]
Continue reading→S Corporation Election
REQUIREMENTS OF S STATUS An S corporation must Be a domestic and eligible corporation Have only one class of stock Have no more than 100 shareholders Have only allowed shareholders (individuals, estates, or qualified trusts) A Non – Resident alien (NRA) may not own shares of S Corp [Must be a citizen / resident […]
Continue reading→S Corporations – Special Taxes
1 Special taxes imposed on S corporations. Passive investment income (PII) tax Built-in gains (BIG) tax LIFO recapture General business credit recapture 1.01 PASSIVE INVESTMENT INCOME(PII) TAX Passive investment income includes gross receipts from royalties, rents, dividends, interest, and annuities. If an S corporation has pre-S corporation E&P (from the period it was a C […]
Continue reading→Auditing Through The Computer
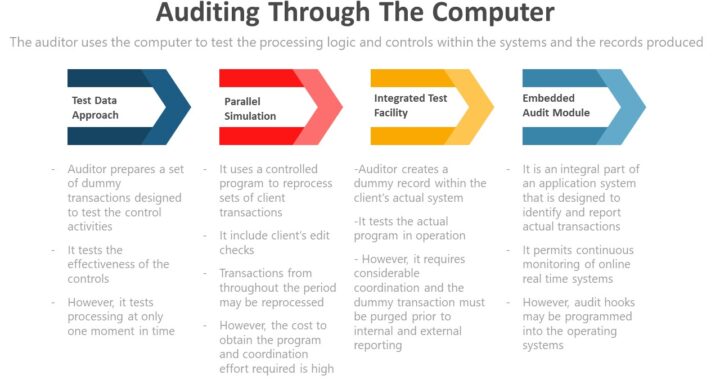
Auditing through the computer – Uses the computer to test the processing logic and controls within the system and the records produced
Test Data Approach – In the test data approach, the auditor prepares a set of dummy transactions specifically designed to test control activities that management claims to have incorporated into the processing programs.
Parallel Simulation – A parallel simulation uses a controlled program (auditor developed program) to reprocess sets of client transactions (real transactions and not dummy) and compares the auditor-achieved results with those of the client.
Integrated Test Facility – Using the integrated test facility (ITF) method, the auditor creates a dummy record within the client’s actual system (e.g., a fictitious employee in the personnel and payroll file). Dummy and actual transactions are processed.
Embedded Audit Module – An embedded audit module is an integral part of an application system that is designed to identify and report actual transactions and other information that meets the criteria of having audit significance (e.g., transactions over $5,000).
If you have found this blog to be useful, you may share with your friends. Thanks!
Purchases-Payables-Cash Disbursement Cycle
Testing of Completeness Assertion for Accounts Payable and Purchases Reconciling total amounts in subsidiary ledgers with the general ledger Performing analytical procedures (e.g., comparing accounts payable turnover with the previous year) Tracing subsequent payments to recorded payables Searching for unvouchered (unsupported) payables Testing of Accuracy Assertion for Accounts Payable and Purchases Obtaining management representation letters […]
Continue reading→Payroll Responsibilities
Duty Department/Individual Provides authorizations of employees and their pay rates – Human resources Oversees employees’ working hours (time cards) – Timekeeping Prepares the payroll register – Payroll Prepares payment vouchers – Accounts payable Approves the payments (signing checks) – Cash disbursement (CFO) Records the payrolls – General ledger If you have found this blog to […]
Continue reading→