Comprehensive Income
Comprehensive income includes all changes in equity of a business during a period except those from investments by and distributions to owners It includes all components of Net Income and Other Comprehensive Income (OCI) Comprehensive Income = Net Income + Other Comprehensive Income Other comprehensive income (OCI) items are: Foreign Currency Translation Adjustments Unrealized […]
Continue reading→Measurement Concepts
Recognition and Measurement Concepts Recognition is the process of formally recording or incorporating an item into the financial statements of an entity as an asset, liability, equity, revenue, or expense Fundamental recognition criteria determine whether and when items should be incorporated into the statements, either initially or as changes in existing items For recognition in […]
Continue reading→Capital Budgeting
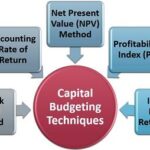
Capital Budgeting Capital budgeting is the process of planning and controlling investments for long-term projects. Many capital budgeting techniques used for screening and preference decisions require the identification of the relevant cash flows for the project. The accounting rate of return is a technique used to assess potential capital projects that ignores the time value […]
Continue reading→Working Capital
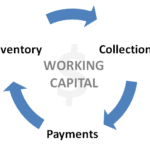
Working Capital Working capital is Current Assets reduced by Current Liabilities Permanent Working Capital is the level of liquid assets that must be maintained regardless of the firm’s level of activity or profitability. As the firm’s needs change on a seasonal basis, temporary working capital is increased or decreased. Working Capital Financing Spontaneous financing is […]
Continue reading→Capital Structure
Core Capital Structure Corporate Capital Structure may be financed by bonds, equity, and preference share capital. Bonds Bonds are the main form of long-term debt financing. It is a formal contract to pay an amount of money to the holder at a certain date. Most bonds provide for a series of cash interest payments on […]
Continue reading→Investment Risk and Return
When analyzing an investment decision, it is important to evaluate the risk attached to the investment. The two basic types of Investment risks are: Systematic Risk – It is the market risk that is faced by all firms. Since all investments are affected, this risk cannot be offset through diversification. Unsystematic Risk – It is […]
Continue reading→Demand and Supply
As necessity is the mother of invention, so is the demand the creation of supply. Law of Demand and its determinants Demand is the willingness and ability of consumers to purchase goods and services at various prices during a period of time. Quantity demanded is the amount that will be purchased at a specific price […]
Continue reading→Fiscal and Monetary Policy
Demand Management through fiscal policy Discretionary fiscal policy is spending that is under the control of individuals within the government. Nondiscretionary fiscal policy is enacted by law. The multiplier effect results from the fact that each dollar spent by a consumer in the economy becomes another consumer’s income and so forth. Keynesian theory calls for […]
Continue reading→Business Cycle and Globalization
Business Cycle The tendency toward instability within the context of overall growth is the business cycle. The cycle has 4 phases: Peak Recession Trough Recovery In addition to identifying the phases of the business cycle, one has to be able to assess the business cycle’s impact on an entity’s operations and its industry. Globalization Business […]
Continue reading→COSO Enterprise Risk Management Framework
The COSO Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework provides a basis for coordinating and integrating all of an organization’s risk management activities. Effective integration (1) improves decision making and (2) enhances performance ERM is based on the premise that every organization exists to provide value to its stakeholders. ERM is defined as “the culture, capabilities, […]
Continue reading→