Estate Income Tax vs Estate Tax
Estate Income Tax Estate Income Tax – Imposed on the income of estates. Imposed on the estate level or beneficiary level An estate (or trust) with a gross income of at least $600 is required to file Form 1041, Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts, no later than the 15th day of the 4th month […]
Continue reading→Gift Tax
The gift tax is a tax of the transfer of a gift imposed on the donor. A gift is complete when the donor has so parted with dominion and control as to leave him or her no power to change its disposition. The amount of a gift made in property is the fair market value […]
Continue reading→Simple and Complex Trusts
Simple Trust – A simple trust is formed under an instrument that (1) requires current distribution of all its income, (2) requires no distribution of the res (i.e., principal, corpus), and (3) provides for no charitable contributions by the trust. Complex Trust – A Complex Trust is a Trust that permits accumulation of current income, […]
Continue reading→Involuntary Conversions
A taxpayer may elect to defer recognition of gain if property is involuntary converted into money or property that is similar or related in service or use. An involuntary conversion of property results from destruction, theft, seizure, requisition, condemnation, or threat of imminent requisition or condemnation. When a property is converted involuntarily into nonqualified proceeds […]
Continue reading→Sale of Principal Residence
Section 121 provided an exclusion upon the sale of a principal residence. No loss may be recognized on the sale of a principal residence. Two tests to qualify for exclusion of gain upon principal residence are: Ownership test – Taxpayer has owned the residence for 2 of the 5 prior years Use test – Taxpayer […]
Continue reading→Like Kind Exchanges
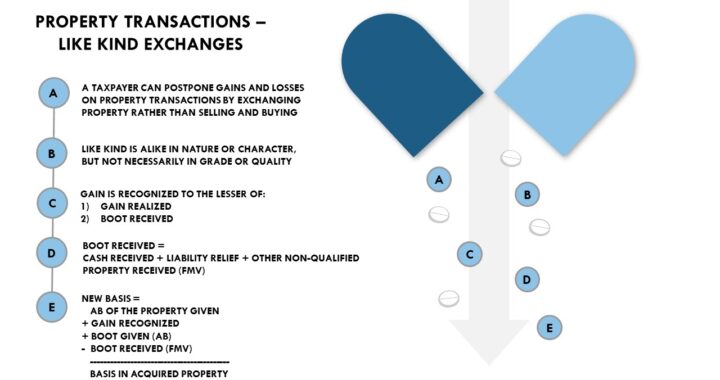
Section 1031 defers recognizing gain or loss to the extent that real property productively used in trade or business or held for production of income (investment) is exchanged for property of like kind. Only real property qualifies for like kind exchange.
Like-kind refers to the nature or character of the property. Real estate for real estate qualifies as a like-kind exchange even if the properties are as different as a rental office building and a parking lot, or even if the properties are located in different states. All other property, including stocks (and other securities and debt instruments) and partnership interests, is excluded from qualifying for like-kind exchange treatment.
Boot is all nonqualified property transferred in an exchange transaction. Boot received includes cash, net liability relief, and other nonqualified property (its FMV).
Recognized Gain = Lesser of gain realized or boot received
Deferred gain = Realized gain – Recognized gain
Deferred loss = Realized loss
Basis of acquired property = AB of property given + Gain recognized+ Boot given – Boot received
OR
Basis of acquired property = FMV of acquired property – Deferred gain + Deferred loss
Related Party Sales
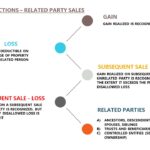
Limited Tax Avoidance Rules limit tax avoidance between related parties. Gain recognized on an asset transfer to a related person in whose hands the asset is depreciable is ordinary income. Loss realized on the sale or exchange of property to a related person is not deductible. Under Sec. 267, losses are not allowed on sales […]
Continue reading→Smart Business Stock Exclusion
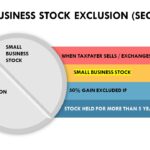
Stock qualifies as Section 1202 stock if it is received after August 10, 1993, the corporation is a domestic C corporation, the seller is the original owner of the stock, and the corporation’s gross assets do not exceed $50 million at the time the stock was issued. Additional requirements do exist. However, the total gross assets […]
Continue reading→Self Employed Business Income and Expenses
Self Employed Business Income and Expenses Self Employment Income is generally reported by Sole proprietors and Independent contractors The three requirements for an expense from a trade or business to be deductible from self-employment income are Ordinary, Necessary, and Reasonable Business Expenses may include: Rent Business Meals Travel Foreign Travel Entertainment Automobile Expenses Taxes Insurance […]
Continue reading→Employee Benefits
Employee Benefits Include the below: Fringe Benefits Employee Discounts De Minimis Qualified Transportation Fringe Benefits Employer-Provided Educational Assistance Employer-Provided Life Insurance Accident and Health Plans Death Benefits Meals and Lodging Incentive Stock Options Cafeteria Plans If you have found this blog to be useful, you may share with your friends. Thanks!
Continue reading→